The Intersection of Technology and Reality: VR, AR, MR
November 5, 2023
Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR) are no longer mere buzzwords of the tech world. They have swiftly emerged as transformative technologies that are reshaping various industries and revolutionizing our daily lives. To truly grasp their significance, it is essential to delve into the depths of these immersive realities and explore their potential. This article aims to shed light on the concepts of VR, AR, and MR, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of their implications and applications.
The advent of VR, AR, and MR has unleashed a wave of possibilities, permeating industries across the spectrum. From healthcare and education to entertainment and manufacturing, these immersive technologies have demonstrated their potential to streamline processes, enhance productivity, and elevate user experiences. Moreover, they have seeped into our everyday routines, changing the way we interact with our surroundings and providing us with novel avenues for communication, exploration, and entertainment.
In this article, we will embark on a journey through the realms of VR, AR, and MR. We will start by demystifying these terms, explaining their fundamental differences, and highlighting their unique characteristics. Following that, we will delve into the profound impact of these immersive technologies on industries, exploring real-world examples of their application and the benefits they bring. Finally, we will reflect on the implications for our daily lives, pondering the potential future developments and challenges that lie ahead.
Now, let us embark on an enlightening exploration of the captivating world of VR, AR, and MR.
Understanding Virtual Reality (VR)
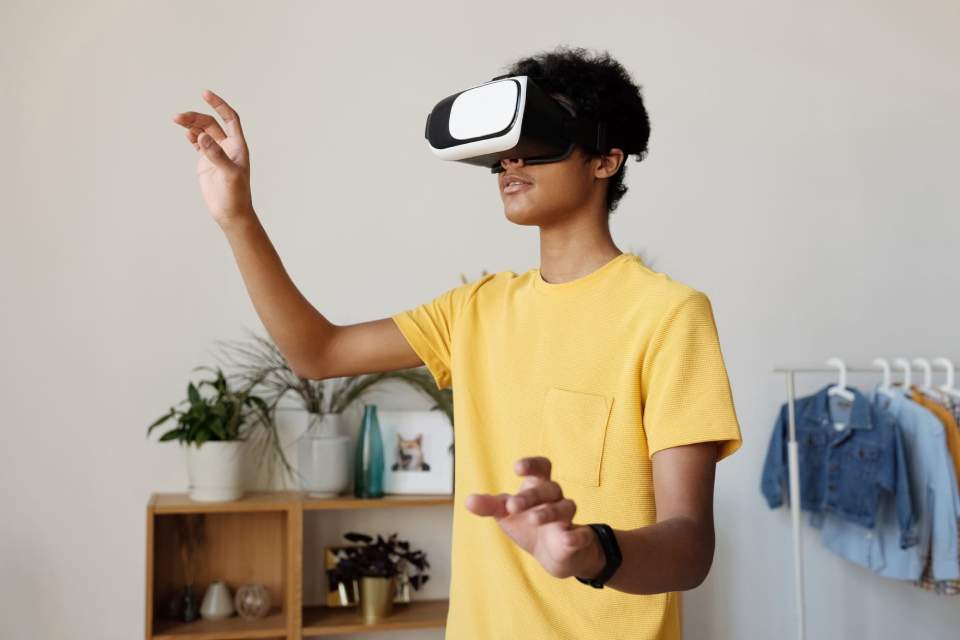
VirtualReality (VR) is a simulated experience that is achieved through computer technology. Through VR headsets such as HTC Vive, Oculus Quest or ValveIndex, it immerses users in a digital experience through encompassing visuals and sounds. The headset and accompanying controllers allow users to navigate through the simulated world using motion tracking. The devices follow their real-world movements, creating a realistic sense of presence within the digital environment. VR has applications in education, medicine, and social sciences -but by far the most widespread application is in the entertainment industry, namely in gaming.
In2020, Valve released a VR game called Half Life: Alyx, where users were set to explore and survive a post-apocalyptic world teeming with alien life. It gained immense popularity throughout the community and won the Best VR/AR Game at TheGame Awards in 2020.
Seeing as we’re in a post-pandemic world, there are opportunities for VR to be adopted more widely in education and business. With programs like Microsoft Teams and Zoom being used as an alternative to meeting at a physical location, many people are looking towards VR technology to produce a more realistic atmosphere to work and learn in. Spatial is a program that allows people to host meetings using VR headsets. Each user has their own avatar and is able to collaborate with others in the virtual space. This technology is an example of the direction that virtual reality is headed in as we enter 2021.
The roots of VR can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers and innovators began experimenting with the concept of simulated environments. The term “virtual reality” was coined in the late 1980s, marking the beginning of a rapid evolution in the technology. Early VR systems relied on bulky headsets, limited graphical capabilities, and rudimentary tracking. However, with advancements in computing power, graphics rendering, and motion tracking, VR has witnessed significant progress, paving the way for more sophisticated and immersive experiences.
Key Components of a VR System
Headsets and Displays
At the core of any VR experience is the headset, which encompasses a high-resolution display and lenses that create a wide field of view. These head-mounted displays (HMDs) come in various forms, such as tethered headsets that connect to a computer and standalone devices that incorporate all the necessary components within the headset itself. The quality of the display, including resolution, refresh rate, and pixel density, greatly impacts the visual fidelity and immersion of the VR experience.
Tracking Systems and Sensors
Accurate tracking is crucial for maintaining the illusion of presence in VR. Tracking systems, often based on infrared or laser technology, capture the user’s movements and translate them into the virtual environment. These systems employ sensors placed in the room or on the user’s body to track their position and orientation, allowing for real-time updates and seamless integration of movements within the digital world.
Input Devices and Controllers
To interact with the virtual environment, users rely on specialized input devices and controllers. These can range from handheld controllers with buttons, triggers, and joysticks to more advanced solutions like gloves or full-body tracking systems. The input devices enable users to manipulate virtual objects, navigate the virtual space, and engage in immersive interactions, adding another layer of realism and interactivity to the VR experience.
Immersive Experiences in Virtual Reality
Visual and Auditory Sensations
One of the primary goals of VR is to provide visually captivating experiences that mimic everyday life or create fantastical environments. High-resolution displays, combined with stereoscopic rendering, ensure a lifelike visual representation, allowing users to perceive depth and three-dimensional objects. Furthermore, spatial audio systems enhance immersion by delivering realistic soundscapes that correspond to the user’s position and movements, heightening the sense of presence within the virtual world.
Interactivity and Presence
A defining characteristic of VR is the interactivity it offers. Users can engage with virtual objects, manipulate them, and even collaborate with others in shared virtual spaces. This interactivity fosters a sense of agency and presence, enabling users to feel like active participants rather than passive observers. The ability to physically move within the virtual environment and interact with objects in a natural and intuitive manner adds to the overall immersion and engagement.
Applications and Use Cases of VR Technology
Gaming and Entertainment
The gaming industry has embraced VR as a groundbreaking medium for immersive gameplay experiences. VR gaming offers players a level of immersion and interaction that goes beyond traditional gaming platforms. Users can step into the shoes of a character, explore virtual worlds, and engage in thrilling adventures, all while feeling a heightened sense of presence and engagement. VR has also expanded beyond gaming, with virtual experiences in movies, virtual theme park rides, and other entertainment applications.
Education and Training
VR has tremendous potential in the field of education and training. It allows students to step into historical events, explore scientific concepts, or visit places that would otherwise be inaccessible. In training scenarios, VR can provide a safe and controlled environment for professionals to practice complex procedures, such as medical simulations or hazardous equipment handling. By providing immersive and realistic experiences, VR enhances learning outcomes and enables users to acquire practical skills in a highly engaging manner.
Simulations and Virtual Environments
Industries such as architecture, engineering, and manufacturing benefit greatly from VR simulations. VR allows designers and engineers to visualize and test their creations before they are built, optimizing the design process and reducing costs. In virtual environments, users can experience realistic simulations of real-world scenarios, such as flight simulators for pilot training or virtual environments for urban planning. These simulations provide a risk-free space for experimentation, training, and evaluation.
Healthcare and Therapy
VR is making significant strides in healthcare, offering innovative solutions for pain management, mental health treatment, and rehabilitation. By immersing patients in calming or distracting virtual environments, VR can alleviate pain and anxiety during medical procedures. Additionally, VR therapy is being explored for treating phobias, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and other mental health conditions. The immersive nature of VR enables therapists to create controlled and personalized environments for exposure therapy and cognitive interventions, leading to more effective outcomes.
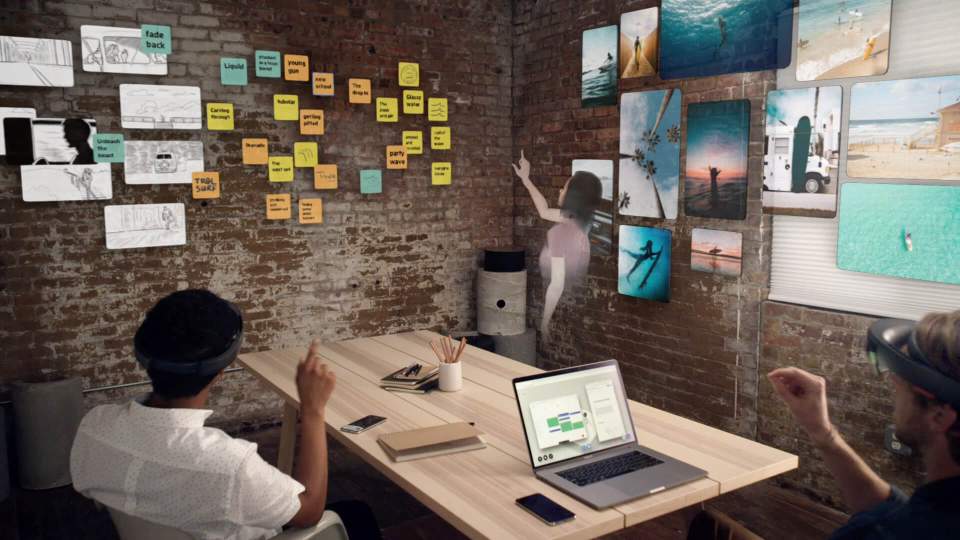

Exploring Augmented Reality (AR)
AugmentedReality (AR) is the enhancement of the physical world through the overlaying of computer-generated content onto the user’s perspective. The content is responsive to the user’s environment, typically to movement or figure recognition. It is arguably the most widely used reality experience today as it is highly accessible for smart device users through camera-based applications, and has gained immense popularity on social media platforms.
One of the main camera features available on Snapchat and Instagram are AR filters where users can alter their appearance and surrounding environment with unique visual effects and sounds. On Instagram, users can produce their own custom filters through programs like Spark AR Studio and add their designs to the library of community-made work to be used by others. IKEA also has a mobile application called IKEA Place where rendered imagery of their products are imposed onto a photograph of a user’s room.
Over the years, Apple has shown invested more and more into their venture with augmented reality. Apple’s iPhone 12 Pro release came with the LiDAR scanner, a feature that allows the phones to quickly 3D map a space including the objects within it. LiDAR makes it simpler for developers to build 3D objects and focus on the creative aspect of projects. Together with their ARkit platform, this scanner has opened new doors for AR experiences to be more easily developed directly on an iOS device.
Differentiating AR from VR and Mixed Reality
While AR shares similarities with VR and Mixed Reality (MR), it is important to understand their distinctions. Unlike VR, which creates a fully immersive virtual world, AR enhances the physical reality by superimposing virtual objects onto it. This allows users to maintain a connection with their physical environment while enjoying additional digital elements. Similarly, AR differs from MR, as MR combines real and virtual elements to create a hybrid environment where physical and digital objects interact in real-time.
Devices and Platforms for AR Experiences
Smartphones and Tablets
One of the most accessible ways to experience AR is through smartphones and tablets. These devices, equipped with high-resolution cameras, powerful processors, and AR-enabled apps, can overlay virtual content onto the tangible world when viewed through the device’s screen. By utilizing the device’s camera and sensors, AR apps can detect the user’s surroundings and accurately place virtual objects within the physical environment, creating an immersive and interactive AR experience.
AR Glasses and Headsets
AR glasses and headsets take the AR experience to a new level of immersion and hands-free convenience. These wearable devices, such as Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap, or Apple’s rumored AR glasses, provide a more natural and seamless AR experience. By projecting virtual content directly into the user’s field of view, AR glasses enable users to interact with digital elements while maintaining awareness of their surroundings. These devices are particularly valuable in professional settings, where hands-free access to information and augmented instructions can enhance productivity and efficiency.
Real-World Applications and Benefits of AR
Industrial and Manufacturing Sectors
AR has found significant applications in industries such as manufacturing, maintenance, and assembly. By overlaying digital instructions, schematics, or visual cues onto physical equipment, AR can guide workers through complex processes, reducing errors and increasing efficiency. AR also enables technicians to access real-time data, perform remote troubleshooting, and collaborate with experts in real-time, resulting in streamlined operations and cost savings.
Retail and E-commerce
AR is revolutionizing the retail landscape by bridging the gap between online and in-store shopping experiences. With AR, customers can visualize products in their own environment before making a purchase. AR-powered virtual try-on solutions allow shoppers to virtually try on clothing, accessories, or even furniture, enhancing the decision-making process and reducing return rates. AR also enables retailers to deliver personalized and interactive shopping experiences, driving customer engagement and boosting sales.
Navigation and Wayfinding
AR is transforming the way we navigate and explore our surroundings. AR navigation apps, such as Google Maps’ Live View, overlay directional cues and information onto the real-world view, making it easier to navigate unfamiliar places. From highlighting points of interest to providing real-time transit information, AR enhances the way we interact with our environment, offering a more intuitive and immersive navigation experience.
Design and Visualization
AR is a game-changer in design and visualization industries. Architects and interior designers can use AR to overlay virtual designs onto physical spaces, allowing clients to visualize and experience the proposed changes in real-time. In product design, AR enables designers to prototype and iterate on 3D models, visualizing how they would appear in real-world contexts. This expedites the design process, fosters better collaboration, and facilitates informed decision-making.
The New IKEA Place App and Apple’s Augmented Reality ARKit
Are you tired of the guesswork when it comes to finding the perfect furniture for your home? Wish there was a way to try before you buy? Well, look no further! We’re thrilled to introduce you to the revolutionary IKEA Place app, designed to transform your home shopping experience.
📲 Available on iPhone 6S and newer models, as well as iPads, IKEA Place allows you to virtually “place” IKEA products in your space using augmented reality (AR) technology. It’s like having your very own interior designer right at your fingertips!
But that’s not all—this incredible app is not limited to just one location. While it’s currently available in the US App Store, IKEA Place will soon be accessible to users around the globe. So, get ready to step into the future of furniture shopping!
🔔 Don’t forget to subscribe to IKEA’s YouTube channel (link provided below) to stay updated with the latest trends and innovations in home decor. We have a lot in store for you!
👉 Subscribe to IKEA here: https://www.youtube.com/@IKEA
Now, let’s dive into the features of IKEA Place that make it a game-changer. Using Apple’s cutting-edge ARKit, this app offers lifelike 3D and true-to-scale models of a wide range of IKEA furnishings. From cozy sofas and stylish armchairs to functional coffee tables and trendy footstools, you can explore and visualize these products within your own home.
No more wondering if that couch will fit in your living room or if the coffee table complements your existing decor. With IKEA Place, you’ll get an accurate impression of the furniture’s size, design, and functionality before making any purchase decisions.
So, what are you waiting for? It’s time to turn your design dreams into reality! Follow these simple steps to get started with IKEA Place:
1️⃣ Ensure your compatible Apple device is updated with iOS 11.
2️⃣ Head to the App Store and search for “IKEA Place.” Download and install the app on your device.
3️⃣ Launch the app, scan your room, and let the magic unfold! Here’s what you can do:
- Explore and search for a wide range of IKEA furnishings (initially focused on sofas, armchairs, tables, footstools, and chairs).
- Experiment with placing furniture in different spots to find the perfect arrangement.
- Capture your creative designs as still images or videos and share them with your loved ones.
- Save your room layouts for future reference or collaborate with others to co-create beautiful spaces.
- Create a personalized list of favorites and conveniently purchase items through the IKEA.com or IKEA Store app.
- Stay updated with the latest product news and get inspired with exciting ideas for enhancing your life at home.
With IKEA Place, you can finally say goodbye to the uncertainty and hello to a new era of home furnishing. Get ready to reimagine your space and unleash your inner designer!
So, what are you waiting for? Click on the link below and start exploring the endless possibilities of IKEA Place.
🔗 More information about IKEA Place: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UudV1VdFtuQ
Video: Say Hej to IKEA Place
Remember, it’s time to stop wondering and start doing. Let IKEA Place transform the way you shop for furniture and create the home you’ve always dreamed of. Happy decorating! 🎉🏡
Over the years, Apple has shown invested more and more into their venture with augmented reality. Apple’s iPhone 12 Pro release came with the LiDAR scanner, a feature that allows the phones to quickly 3D map a space including the objects within it. LiDAR makes it simpler for developers to build 3D objects and focus on the creative aspect of projects. Together with their ARkit platform, this scanner has opened new doors for AR experiences to be more easily developed directly on an iOS device.

Unveiling Mixed Reality
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, we find ourselves on the brink of a new era of immersive experiences. One such groundbreaking development is the advent of mixed reality.
In this section, we will explore the fascinating world of mixed reality, diving into its definition, concept, and the multitude of ways it is transforming various industries.
MixedReality (MR) combines elements of both VR and AR into one experience. It resembles AR in the way that the technology imposes generated imagery into the user’s view, but has the key difference of the digital content co-existing with the physical world in real-time. This difference means users are able to interact with MR objects as if it was a real-life object and manipulate its state.
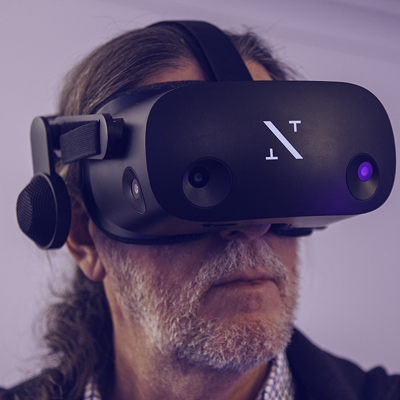
The most popular example of this technology is the HoloLens, a mixed reality headset byMicrosoft. With the headset being priced at $5000AUD it’s not a trendy product aimed at consumer use, but is instead aimed at enterprises who will use the device as a business tool to build their own applications and to help the organisation work more effectively. The HoloLens offers some impressive features that are reminiscent of what we’ve seen in sci-fi movies.
For example, the device has built-in eye tracking software that can be used to follow the pace of a user’s reading and adjust the speed of the text’s flow accordingly. The device also has precise hand and finger tracking to make navigating through detailed interfaces easy for users.
At its core, mixed reality strives to blur the boundaries between the physical and digital worlds, enabling users to interact with digital content in a more natural and intuitive manner. By seamlessly integrating virtual objects into the actual environment, mixed reality opens up a world of possibilities for enhanced collaboration, creativity, and problem-solving.
Merging Virtual and Real-World Elements
The magic of mixed reality lies in its ability to merge virtual and real-world elements seamlessly. Through advanced technologies such as spatial mapping, depth sensing, and object recognition, mixed reality devices, such as headsets or smart glasses, can scan the environment and accurately place virtual objects within it. This merging of the virtual and physical worlds creates a compelling and immersive experience that captivates users and enhances their perception of reality.
Continuum of Mixed Reality Experiences
Mixed reality experiences can be categorized along a continuum, ranging from purely virtual to completely real-world interactions. This continuum is often referred to as the Mixed Reality Spectrum. At one end, we have virtual reality experiences, where users are fully immersed in a digitally created environment. Moving along the spectrum, we encounter augmented reality, where virtual content is overlaid onto the material realm. Finally, at the other end, we find mixed reality, where virtual and real-world elements coexist and interact in real-time.
Examples and Use Cases of Mixed Reality
Architecture and Interior Design
In the realm of architecture and interior design, mixed reality is revolutionizing the way professionals conceptualize and showcase their designs. With mixed reality, architects and designers can create virtual 3D models of buildings or spaces and visualize them in the physical realm. This enables clients to experience the proposed designs firsthand, walking through virtual rooms, assessing proportions, and even making real-time changes. By bridging the gap between imagination and reality, mixed reality empowers architects and interior designers to bring their visions to life.
Engineering and Prototyping
For engineers and product designers, mixed reality offers invaluable tools for prototyping and visualization. By overlaying virtual models onto physical objects, engineers can analyze and manipulate complex machinery or components with ease. This not only expedites the design process but also allows for efficient collaboration and rapid iterations. Through mixed reality, engineers can gain a deeper understanding of their creations, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions before bringing their designs to fruition.
Collaborative Workspaces
Collaboration lies at the heart of success in many industries, and mixed reality is transforming the way teams work together. With shared mixed reality environments, colleagues from different locations can come together virtually, overcoming geographical barriers and collaborating in real-time. Whether it’s brainstorming ideas, reviewing designs, or conducting virtual meetings, mixed reality provides an immersive and interactive platform that fosters creativity and enhances productivity.
Cultural and Historical Preservation
Mixed reality also has the power to preserve and bring history and culture to life. Museums and cultural institutions can leverage mixed reality to create immersive experiences for visitors, allowing them to step back in time and explore ancient civilizations or significant historical events. By superimposing digital artifacts onto real-world settings, mixed reality enables us to engage with history in a whole new way, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation for our collective heritage.

Industries Transformed by VR, AR, and Mixed Reality
In recent years, the advent of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) has not only captured our imaginations but has also revolutionized various industries.
In this section, we will delve into the profound impact of VR, AR, and MR on different sectors, exploring the innovative ways in which these technologies have transformed the landscape.
Gaming and Entertainment
Immersive Gaming Experiences
The gaming industry has been at the forefront of adopting VR, AR, and MR technologies, providing gamers with unparalleled immersive experiences. With VR headsets and controllers, players can step into virtual worlds, interacting with lifelike characters and environments. The sense of presence and engagement offered by VR gaming creates an entirely new level of excitement and realism, transporting players into captivating digital realms.
Virtual Reality Arcades and Theme Parks
Beyond home gaming setups, virtual reality arcades and theme parks have emerged, offering individuals the opportunity to try VR experiences that may be beyond their reach at home. These dedicated spaces provide state-of-the-art VR equipment and a wide selection of games and simulations, attracting both gaming enthusiasts and curious newcomers. Virtual reality arcades and theme parks have become popular destinations, fostering social interactions and expanding the horizons of entertainment.
Education and Training
Virtual Classrooms and Remote Learning
VR, AR, and MR have also made significant strides in the field of education. Virtual classrooms and remote learning platforms leverage these technologies to create engaging and interactive learning environments. Students can explore historical sites, travel to distant countries, or even embark on virtual science experiments. The immersive nature of VR, AR, and MR enhances comprehension and retention, making complex subjects more accessible and captivating.
Simulation-Based Training Programs
In professions that require practical training, VR, AR, and MR have proven to be game-changers. Simulations allow trainees in fields such as aviation, military, and emergency response to practice real-life scenarios in a safe and controlled environment. Surgeons can refine their skills using virtual surgical simulations, while firefighters can train for hazardous situations without exposing themselves to actual risks. These immersive training programs not only enhance skills but also improve decision-making under pressure.
Healthcare and Medicine
Surgical Planning and Training
The healthcare industry has embraced VR, AR, and MR technologies to revolutionize surgical planning and training. Surgeons can use virtual reality to visualize complex procedures before stepping into the operating room, improving precision and reducing risks. Medical students can also benefit from realistic surgical simulations, allowing them to practice intricate techniques without the need for live patients. These technologies are reshaping the future of surgery, enhancing patient outcomes and advancing medical education.
Pain Management and Rehabilitation
In the realm of pain management and rehabilitation, VR, AR, and MR have demonstrated their potential to alleviate discomfort and expedite recovery. By immersing patients in virtual environments or overlaying digital content on real-world therapy sessions, these technologies offer distractions and positive stimuli, reducing pain perception and promoting relaxation. Additionally, virtual environments can be utilized for rehabilitation exercises, encouraging patients to engage in therapy while making the process more enjoyable and motivating.
Architecture and Design
Virtual Walkthroughs and 3D Modeling
For architects and designers, VR, AR, and MR have transformed the way projects are visualized and presented. With virtual walkthroughs, clients can explore and experience architectural designs before construction even begins. Detailed 3D models can be created and manipulated, allowing stakeholders to understand spatial relationships, assess design elements, and make informed decisions. These technologies have streamlined the design process, fostering collaboration and minimizing costly revisions.
Visualization of Building Plans and Concepts
Moreover, VR, AR, and MR have become indispensable tools for showcasing building plans and concepts to clients and investors. Using augmented reality, architects can superimpose virtual structures onto real-world environments, enabling stakeholders to visualize the finished project in situ. This immersive experience provides a deeper understanding of the design vision and allows for valuable feedback, resulting in more accurate representations and informed decision-making.
Marketing and Advertising
Augmented Reality Campaigns and Product Visualization
In the realm of marketing and advertising, AR has opened up exciting possibilities for engaging with consumers in innovative ways. Brands can create augmented reality campaigns that overlay digital content onto real-world environments, blurring the line between physical and digital experiences. This interactive approach captures attention, fosters brand awareness, and drives customer engagement. Furthermore, product visualization in AR allows customers to see how furniture, clothing, or cosmetics would look in their own spaces, enhancing the shopping experience and reducing purchase uncertainty.
Virtual Showrooms and Interactive Experiences
With VR, companies can create virtual showrooms, enabling customers to explore products in a virtual space. Automotive manufacturers, for instance, can provide virtual test drives that simulate the driving experience, allowing potential buyers to interact with different car models without leaving their homes. Additionally, interactive experiences, such as branded games or immersive storytelling, captivate audiences and forge memorable connections with brands. VR, AR, and MR have become powerful tools for marketers to create unique and compelling experiences that leave a lasting impact.
Technological Advancements and Future Possibilities
VR is most commonly seen as a channel for entertainment, but at 42 Interactive we’ve been exploring the possibilities of virtual reality in the social sciences area. We’ve been working on InstacalmVR, a virtual relaxation therapy experience that assists users with mindful meditation. It guides users through five unique journeys using narration and imagery to help achieve deep relaxation. The simulated experience has been designed with the guidance of a clinical psychologist in order to help us offer the best therapeutic journey.
As virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) continue to evolve at a rapid pace, exciting technological advancements are shaping the future of these immersive technologies.
In this section, we will explore the ongoing developments in VR, AR, and MR, the improvements in hardware and software capabilities, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, the potential impact on various industries and society, and delve into speculations on the future of immersive technologies.
Ongoing Developments in VR, AR, and Mixed Reality
The field of VR, AR, and MR is characterized by constant innovation and continuous development. Companies and researchers are consistently pushing the boundaries of what is possible, refining existing technologies, and introducing new concepts. Advancements in display technologies, tracking systems, and input devices are enhancing the immersive experience, striving for higher levels of realism and interactivity. Ongoing developments in areas such as haptic feedback, eye-tracking, and gesture recognition are further enriching the user’s interaction with virtual and augmented environments.
Improvements in Hardware and Software Capabilities
One of the key drivers of progress in VR, AR, and MR is the continual improvement in hardware and software capabilities. Powerful processors, high-resolution displays, and advanced graphics processing units (GPUs) are enabling more realistic and visually stunning virtual and augmented experiences. The miniaturization of hardware components has led to the development of lighter and more comfortable headsets, making extended use more accessible and enjoyable. Additionally, the evolution of software platforms and development tools is facilitating the creation of more sophisticated and immersive applications, empowering developers to bring their ideas to life.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into VR, AR, and MR opens up a realm of possibilities. AI algorithms can enhance user interactions by intelligently adapting to user preferences, predicting behavior, and personalizing experiences. Machine learning techniques can be employed to create realistic simulations, generate lifelike characters, and automate complex tasks. AI and ML also enable real-time data analysis and interpretation, allowing for dynamic and adaptive content delivery based on user input and environmental factors.
Potential Impact on Various Industries and Society
The potential impact of VR, AR, and MR extends far beyond entertainment and gaming. These immersive technologies have the potential to revolutionize industries such as healthcare, education, manufacturing, architecture, and more. In healthcare, surgeons can perform complex procedures with greater precision through VR simulations, while AR can assist in providing real-time information during surgeries. In education, VR and AR can create immersive learning environments, enabling students to explore historical events or experience scientific phenomena. In manufacturing, MR can streamline design processes and enhance collaboration between teams. The impact of VR, AR, and MR on society is not limited to specific industries; it has the potential to reshape the way we communicate, work, and interact with the world around us.
Speculations on the Future of Immersive Technologies
Looking ahead, the future of immersive technologies holds immense possibilities. As hardware becomes more compact and affordable, we can anticipate widespread adoption and integration of VR, AR, and MR into our daily lives. Advancements in neurofeedback and brain-computer interfaces may lead to direct neural connections with virtual environments, blurring the line between the physical and the digital. The integration of haptic feedback and scent technologies may add additional sensory dimensions to immersive experiences. Furthermore, the potential synergies between VR, AR, and MR with other emerging technologies, such as 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics, can unlock new avenues of innovation and transformation.
Challenges and Considerations
As virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies continue to evolve and gain momentum, it is important to address the challenges and considerations that come along with their widespread adoption.
In this section, we will explore the technical limitations and constraints, ethical and privacy concerns, accessibility and inclusivity in immersive experiences, as well as regulatory and legal considerations.
Technical Limitations and Constraints
Display Resolution and Field of View
One of the primary technical challenges in VR, AR, and MR is achieving high display resolution and a wide field of view. Users expect crisp, detailed visuals that closely resemble the actual environment. However, current hardware limitations can result in pixelation or blurriness, which can compromise the immersive experience. Additionally, the field of view determines the extent of the virtual or augmented content visible to the user. Expanding the field of view without sacrificing quality remains a significant technical hurdle.
Processing Power and Latency Issues
Creating convincing and seamless immersive experiences requires substantial processing power. The rendering of complex virtual environments, tracking user movements in real-time, and delivering responsive interactions demand significant computational resources. Overcoming processing power limitations while minimizing latency— the delay between user input and system response—is crucial to prevent motion sickness and maintain a sense of presence within the virtual or augmented space.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Data Collection and User Privacy
VR, AR, and MR applications often rely on collecting user data to personalize experiences, improve performance, and deliver targeted content. However, this data collection raises ethical concerns regarding user privacy. It is crucial for companies to be transparent about the data they collect, how it is used, and to obtain informed consent from users. Striking a balance between personalization and privacy protection is essential to foster user trust in these technologies.
Psychological and Societal Implications
The immersive nature of VR, AR, and MR can have psychological and societal implications. Extended exposure to virtual environments may affect users’ perception of reality and their ability to distinguish between the virtual and physical worlds. Moreover, the potential for addiction or dependence on these technologies requires careful consideration. Understanding the psychological impact and promoting responsible usage is crucial to ensure a healthy relationship between users and immersive experiences.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Immersive Experiences
As VR, AR, and MR technologies gain prominence, it is essential to address accessibility and inclusivity challenges. Factors such as physical disabilities, cognitive impairments, and socioeconomic disparities can hinder individuals from fully experiencing these technologies. Designing inclusive experiences that cater to a diverse range of users and considering accessibility features, such as closed captions, audio descriptions, and adaptive interfaces, are imperative to ensure equal opportunities for everyone.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
The rapid advancement of VR, AR, and MR technologies necessitates regulatory and legal frameworks to address potential issues. Intellectual property rights, content licensing, safety standards, and privacy regulations are some of the areas that require attention. Policymakers and industry stakeholders must collaborate to establish guidelines that protect consumer interests, foster innovation, and maintain ethical standards in the development and deployment of immersive technologies.
Case Studies and Success Stories
In the realm of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), there are numerous examples of innovative applications that have left a lasting impact. These case studies and success stories highlight the transformative power of immersive technologies across various industries. By examining these examples, we can glean valuable insights and uncover best practices that contribute to their success.
Notable Examples of VR, AR, and Mixed Reality Applications
VR in Healthcare: Surgical Training and Patient Care
Virtual reality has revolutionized surgical training, allowing surgeons to practice complex procedures in a realistic and risk-free environment. Companies like Osso VR have developed immersive simulations that help surgeons refine their skills and enhance patient safety. VR has also been utilized in pain management, providing patients with immersive experiences to distract them from discomfort during medical procedures.
AR in Retail: Enhancing Customer Experiences
Augmented reality has reshaped the retail industry by offering unique and interactive customer experiences. IKEA’s Place app, for instance, allows users to visualize furniture in their own space before making a purchase. By overlaying digital information onto the material world, AR enables customers to make informed decisions, increases engagement, and reduces return rates.
MR in Architecture and Design: Virtual Walkthroughs and Collaboration
Mixed reality has proven valuable in architecture and design, enabling professionals to visualize and interact with virtual models in real-world contexts. Firms like Trimble have developed applications like SketchUp Viewer, which allows architects and clients to experience virtual walkthroughs of building designs. MR also facilitates collaborative workspaces where multiple users can view and manipulate virtual objects simultaneously, regardless of their physical locations.
Impact on Specific Companies or Industries
Entertainment Industry: Immersive Gaming and Theme Parks
The entertainment industry has witnessed a significant impact from VR and AR. Companies like Oculus and HTC Vive have pioneered immersive gaming experiences, transporting players into captivating virtual worlds. Theme parks have also integrated VR and AR technologies to enhance attractions and provide visitors with unforgettable experiences, such as Disney’s Star Wars: Galaxy’s Edge.
Education and Training: Virtual Classrooms and Simulation-Based Learning
The education and training sector has embraced immersive technologies to revolutionize learning experiences. Virtual classrooms and remote learning platforms enable students to engage with educational content from anywhere in the world. Simulation-based training programs in fields like aviation and healthcare offer a safe and controlled environment for practical learning, allowing trainees to develop critical skills.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
User-Centric Design: Prioritizing User Experience
The success of VR, AR, and MR applications lies in their ability to provide seamless and intuitive user experiences. User-centric design is paramount, emphasizing the importance of user research, iterative testing, and feedback integration. Developers must prioritize ease of use, comfort, and accessibility to ensure widespread adoption and positive reception.
Content Relevance and Contextual Integration
Successful immersive experiences are those that seamlessly integrate virtual elements with real-world contexts. Content relevance is crucial to engage users and provide meaningful interactions. Understanding the specific needs and preferences of the target audience allows developers to deliver compelling and contextually relevant content.
Collaboration and Industry Partnerships
Collaboration between technology developers, content creators, and industry experts is a key factor in driving the success of immersive applications. By fostering partnerships, sharing knowledge, and leveraging expertise from different domains, companies can unlock new possibilities and overcome challenges collectively.
Adoption and Consumer Readiness
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the adoption of new innovations plays a pivotal role in their success. When it comes to virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), understanding market trends, consumer attitudes, and the barriers to widespread adoption is essential. This article explores the current state of adoption and consumer readiness, shedding light on key factors that influence the integration of these immersive technologies.
Market Trends and Adoption Rates
The market for VR, AR, and MR has experienced significant growth in recent years. The global market size for these technologies is projected to reach billions of dollars by the end of the decade. Technological advancements, increased investment, and expanding use cases across industries have contributed to this upward trajectory.
Adoption rates vary across different sectors. Gaming and entertainment have been early adopters of VR, with immersive gaming experiences and virtual reality arcades captivating audiences. In industries like healthcare, education, and architecture, the adoption of VR, AR, and MR has gained momentum due to their potential to revolutionize training, visualization, and collaboration.
Consumer Attitudes and Perceptions
Consumer attitudes towards immersive technologies have evolved over time. Initially viewed as niche and futuristic, VR, AR, and MR are now becoming more mainstream. Consumers are increasingly recognizing the value and potential of these technologies in various aspects of their lives.
Perceptions of VR, AR, and MR differ among individuals. Some embrace the immersive experiences and see them as a gateway to new possibilities, while others may still harbor skepticism or perceive them as complex and intimidating. However, as technology continues to advance and user-friendly applications become more prevalent, consumer attitudes are gradually shifting towards curiosity and acceptance.
Barriers to Widespread Adoption
Despite the growing interest and enthusiasm, several barriers hinder the widespread adoption of VR, AR, and MR technologies. These include:
- Cost and Accessibility: High-end VR and AR devices can be expensive, limiting accessibility for some consumers. Additionally, the requirement of powerful hardware and software compatibility poses challenges for widespread adoption.
- Content Quality and Variety: The availability of high-quality and diverse content is crucial for engaging users. A lack of compelling and immersive experiences may dampen consumer interest and impede adoption.
- User Comfort and Experience: Factors like motion sickness, discomfort from wearing headsets, and the need for continuous improvement in ergonomics can impact user comfort and satisfaction.
- Limited Awareness and Education: Many consumers still have limited knowledge and understanding of VR, AR, and MR technologies. Educating the public about the potential benefits and addressing misconceptions can help overcome this barrier.
Strategies for Successful Integration
To foster successful integration of VR, AR, and MR technologies, several strategies can be employed:
- Enhancing Affordability and Accessibility: Continued efforts to reduce the cost of devices and increase accessibility through user-friendly interfaces and compatibility with a broader range of platforms.
- Diversifying Content Offerings: Investing in the development of high-quality, immersive content across various industries and applications to cater to diverse consumer interests and needs.
- Prioritizing User Experience: Designing intuitive and comfortable user experiences that minimize discomfort, optimize performance, and provide seamless interactions.
- Educating and Engaging Consumers: Conducting awareness campaigns, demonstrations, and educational initiatives to familiarize consumers with the potential applications and benefits of immersive technologies.
Conclusion
As the tech industry grows, we’ll be seeing more uses and applications of these technologies in our day today lives. With constant advancements being developed, we can’t wait to see what’s next in this exciting area of technology.
Throughout this article, we delved into the captivating world of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). We explored their definitions, examined how virtual and real-world elements merge in these immersive experiences, and discussed the continuum of mixed reality experiences. Additionally, we explored a wide range of examples and use cases across industries, including architecture and interior design, engineering and prototyping, collaborative workspaces, and cultural and historical preservation.
Final Thoughts on the Transformative Potential of VR, AR, and Mixed Reality
The transformative potential of VR, AR, and mixed reality cannot be overstated. These technologies have revolutionized how we perceive and interact with our surroundings, opening up a realm of possibilities for industries and individuals alike. From immersive gaming experiences that transport us to fantastical worlds to virtual classrooms that transcend geographical boundaries, the impact of these technologies is profound.
Moreover, advancements in hardware and software capabilities, coupled with the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, have paved the way for even more sophisticated and realistic experiences. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can anticipate further breakthroughs and innovations that will shape the future of how we learn, work, play, and connect.
As we conclude this exploration of VR, AR, and mixed reality, it is important to emphasize the value of further exploration and adoption. These immersive technologies hold immense potential for businesses, individuals, and society as a whole. By embracing them and harnessing their capabilities, we can unlock new avenues for creativity, productivity, and engagement.
For businesses, integrating VR, AR, and mixed reality can provide a competitive edge, enabling them to showcase products and services in innovative ways, streamline workflows, and deliver memorable experiences to their customers. Individuals can benefit from enhanced learning opportunities, immersive entertainment, and improved collaboration in various fields.
To fully embrace the transformative power of VR, AR, and mixed reality, it is essential for stakeholders to stay informed about the latest developments, participate in the ongoing discourse, and actively explore how these technologies can be harnessed to meet their specific needs.
Are you feeling stressed and in need of a moment of tranquility?
Discover a world of tranquility with Neurotechnology’s InstacalmVR™ v2.0. Immerse yourself in a serene and rejuvenating experience right from home. Find solace in this guided journey, combining VR and soothing narration for deep relaxation. Experience the transformative power of virtual relaxation therapy.
Learn more on their website or find it on the Steam store.
Website: https://neurotechnology.com.au/instacalmvr-virtual-relaxation-therapy/
Get it from Steam store here: https://store.steampowered.com/app/1153860/Instacalm_VR/
Take a step towards inner peace, click the link and watch the video now.
Video: Neurotechnology InstacalmVR ™ v2.0 - White Room Virtual Relaxation Therapy
Share your thoughts with us: What features would youlike to see introduced in the next few years?
Written by Amy Vuong, Isna Firdaus, Leonis Purba










